Design of Earthing Grid
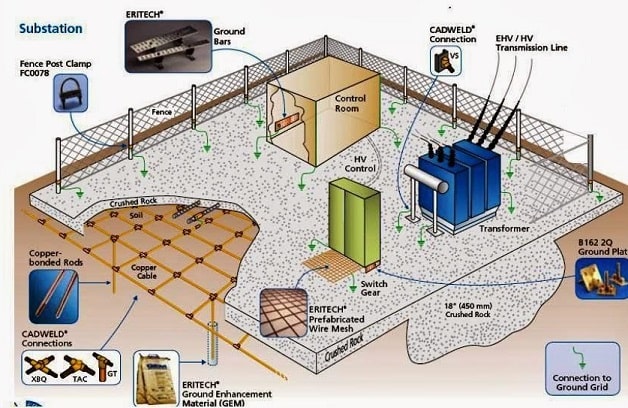
Design of Earthing Grid
In high and medium voltage Air Insulated Substations (AIS) the electromagnetic field, which causes are the static charges of bare cable and conductors and by the atmospheric conditions (surges), induce voltages at no-live parts of the installation that create potential differences between metallic parts and ground and also between different points of the ground.
These potential differences give origin to step potential and touch potential, or a combination of both, that can lead to circulation of an electric current through the human body, that can cause hazardous to people.
Touch voltage (Et) can be defined as the maximum potential difference that exists between an earthed metallic structure capable to be touched by the hand and any point of the ground, when a fault current flows. It is usual to consider a distance of 1 m between the metallic structure and the point on the ground. Step voltage (Es) is defined as the maximum potential difference that exists between the feet when a fault current flows.
Do you need help with Protech Earthing

Copper Rod

GI Electrode

Copper Electrode





